Complementarity! The development of communication mode and the potential of smart meters
Smart meters, which basic function is metering, according to the developement of smart grid and market application demand derive many functions. Especially the two-way communication function is the soul of smart grid digitalization, refinement, and intelligent management, which gives the meter more missions through communication carriers allows humans and smart meters to interact with information, such as seting parameters, reading power consumption data, reporting event alarms, issuing control commands, and upgrading firmware.
1. WAN mode refers to the communication method used by smart meters to directly interact with the system platform for data interaction, including GPRS, NB-IOT, WiFi, Ethernet, optical fiber, etc.
 | 1.1. GPRS communication: GPRS communication, the most used communication method by smart meters, In general, GPRS communication has high reliability but with operating costs. 1.2. NB-IoT communication: NB-IoT (Narrow Band Internet of Things) communication, which uses communication 1.3. WiFi, Ethernet, optical fiber communication: They are the internet network communication, with fast transmission rate. |
2.LAN mode refers to the data connection between the communication method used by the smart meter and the centralized controller, and then the centralized controller interacts with the system platform through the communication mode of the WAN class, including PLC, LoRa, Zigbee, etc.
2.1. PLC communication: PLC (power line carrier) communication,which uses existing In general, the advantages of PLC communication are easy installation,no need 2.2. LoRa communication: LoRa communication is a wireless modulation method, 2.3. Zigbee communication: Zigbee is a low-speed short-distance wireless network protocol, The LAN communication methods used by smart meters are | 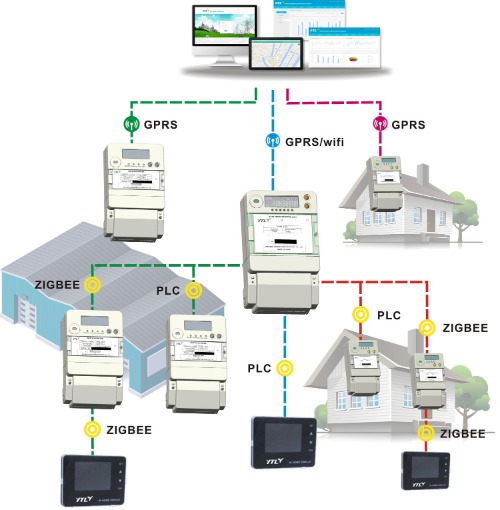 |
In order to adapt to different installation environments and communication requirements of different countries, smart meters will use a variety of communication methods; When we develop and design, the communication module is easily replaced in the field, hot-swappable and safely isolated. Smart meters transmit data to the system platform in real time through communication functions, which provides a basis for data analysis for the improvement of electricity quality and the development of smart grid, and guides the direction of improvement.

Comments
Post a Comment